Public health, explained: Sign up to receive Healthbeat’s free New York City newsletter here.
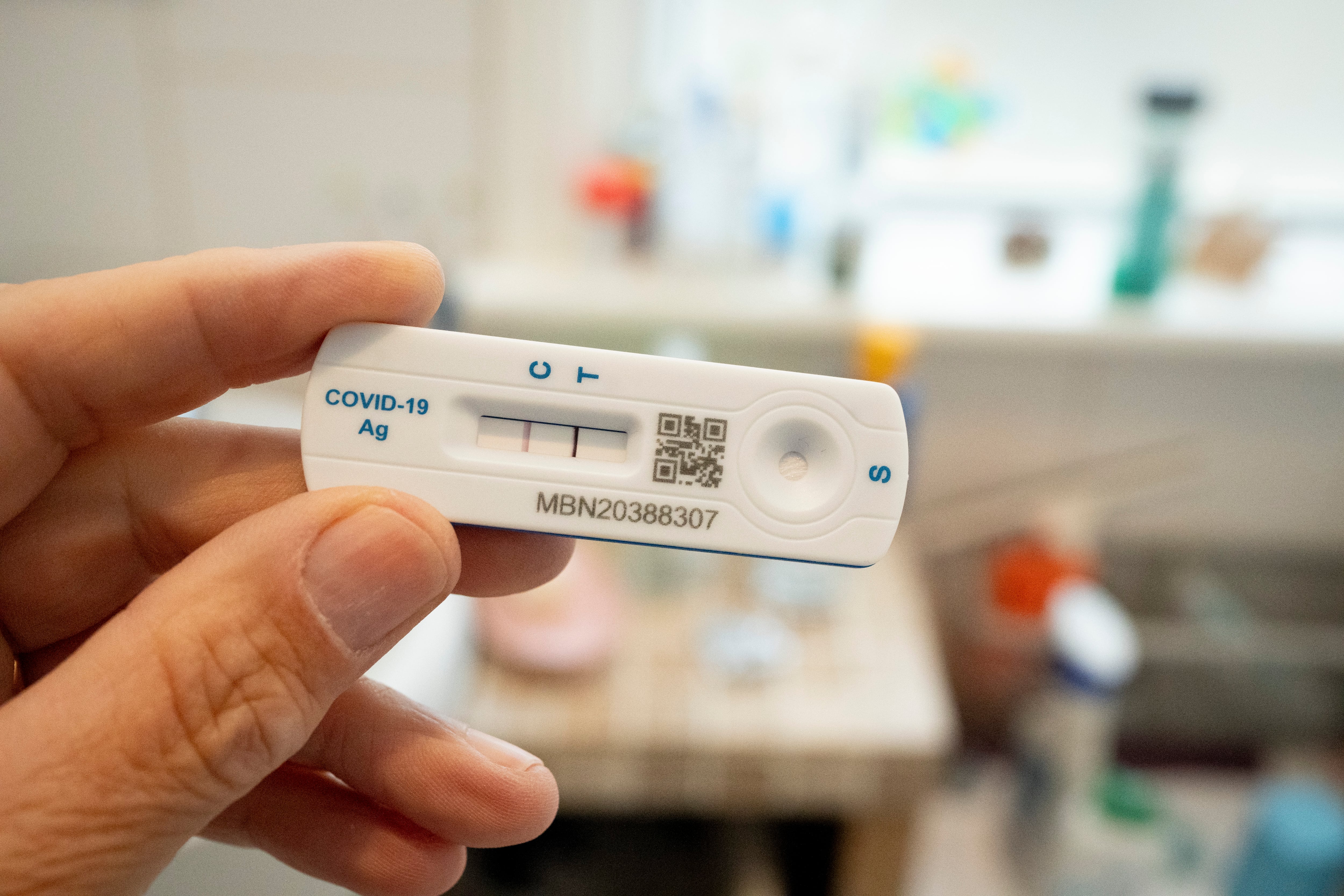
Covid-19 is on the rise in New York and across much of the United States this summer.
In recent years, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has significantly shifted its guidance for people who test positive for Covid-19. In 2021, the CDC shortened its recommended isolation period for people with Covid-19 to five days, down from 10 days, in most cases. The agency’s guidance became even less restrictive this year, though some public health experts urge stricter measures to stop the spread of disease.
Here’s what you need to know if you test positive.
How long should you isolate?
The CDC recommends a two-part approach if you test positive.
First, you should stay home when sick. You can resume normal activities if your symptoms are improving overall and you have not had a fever for 24 hours (without taking fever-reducing medications).
Second, when you end isolation, you should take preventative measures for the next five days, including physical distancing, air purification, masking, and testing when around other people indoors.
Some public health experts recommend taking stricter measures to ensure that you are not infecting others. Katelyn Jetelina, an epidemiologist, Healthbeat partner, and author of the “Your Local Epidemiologist” newsletter, says the best approach is to isolate until your at-home Covid-19 test is negative, which could range from three to 15 days. And if you must leave isolation beforehand, she urges wearing an N95 mask.
Dr. Bruce Y. Lee, a professor at the CUNY Graduate School of Public Health & Health Policy, recommends erring on the side of caution, particularly to protect vulnerable people around you.
“The bottom line is, a lot of the original aspects of the virus still hold,” he said. “There are people that remain contagious after five days, or after two days, or three days, and that’s what should guide isolation. If you’re still contagious, you can still pass it on to someone else.”
How do you get tested?
Four years into the pandemic, much of the Covid-19 testing infrastructure in New York and across the country has faded away.
In New York, residents can find rapid and PCR testing at NYC Health + Hospitals facilities and community care clinics.
Pharmacies sell rapid test kits, typically for about $12 per test. But private insurers are no longer required to cover the cost of tests.
The federal government has resumed its Covid-19 test kit program, which mails free tests to Americans.
Should you take Paxlovid?
The antiviral medication Paxlovid is available for anyone ages 12 and older who is at high risk of developing severe Covid-19 — and particularly for people who are at least 65 years old.
Anyone who tests positive for Covid-19 should see if they are eligible for Paxlovid, said Dr. Sean T. Liu, the medical director of Mount Sinai’s COVID Clinical Trials Unit and an associate professor of medicine at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Paxlovid is effective when taken within the first five days of developing symptoms.
“The faster you get the Paxlovid, the more effective it is,” Liu said. “It’s a timing thing.”
New Yorkers can call the city’s Covid-19 hotline (212-COVID19) to connect with a NYC Health + Hospitals clinician who can prescribe antiviral medication, according to Patrick Gallahue, a spokesperson for the Health Department.
Eliza Fawcett is a reporter covering public health in New York City for Healthbeat. Contact Eliza at efawcett@healthbeat.org.