Public health, explained: Sign up to receive Healthbeat’s free Atlanta newsletter here.
An unvaccinated metro Atlanta resident has tested positive for measles, the first case in Georgia this year of one of the most contagious vaccine-preventable diseases.
In a press release, the Georgia Department of Public Health announced Tuesday that the patient caught the airborne disease while traveling within the United States. The person was contagious between Jan. 19 and 24, and the agency is working to find residents who may have been exposed during that time.
The patient’s age and travel locations were not announced.
Last year, the department detected six measles cases in Georgia. It’s one of the highest recorded case totals over the past 10 years — second only to 2019, when a Cobb County outbreak contributed to 18 state cases. Most of those years, the agency detected no cases.
Researchers have repeatedly found that the disease’s vaccine — which protects against measles, mumps and rubella — is effective at preventing new infections. One dose prevents 93% of infections, and two doses prevent 97% of possible measles cases, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Childhood uptake of the MMR vaccine has declined in the United States and Georgia over the past few years. Some 88.4% of Georgia kindergartners had received the shot in the 2023-24 school year compared to 94% a decade earlier, according to the CDC. The state’s laws allow students in schools to receive religious and medical exemptions from their childhood vaccination requirements.
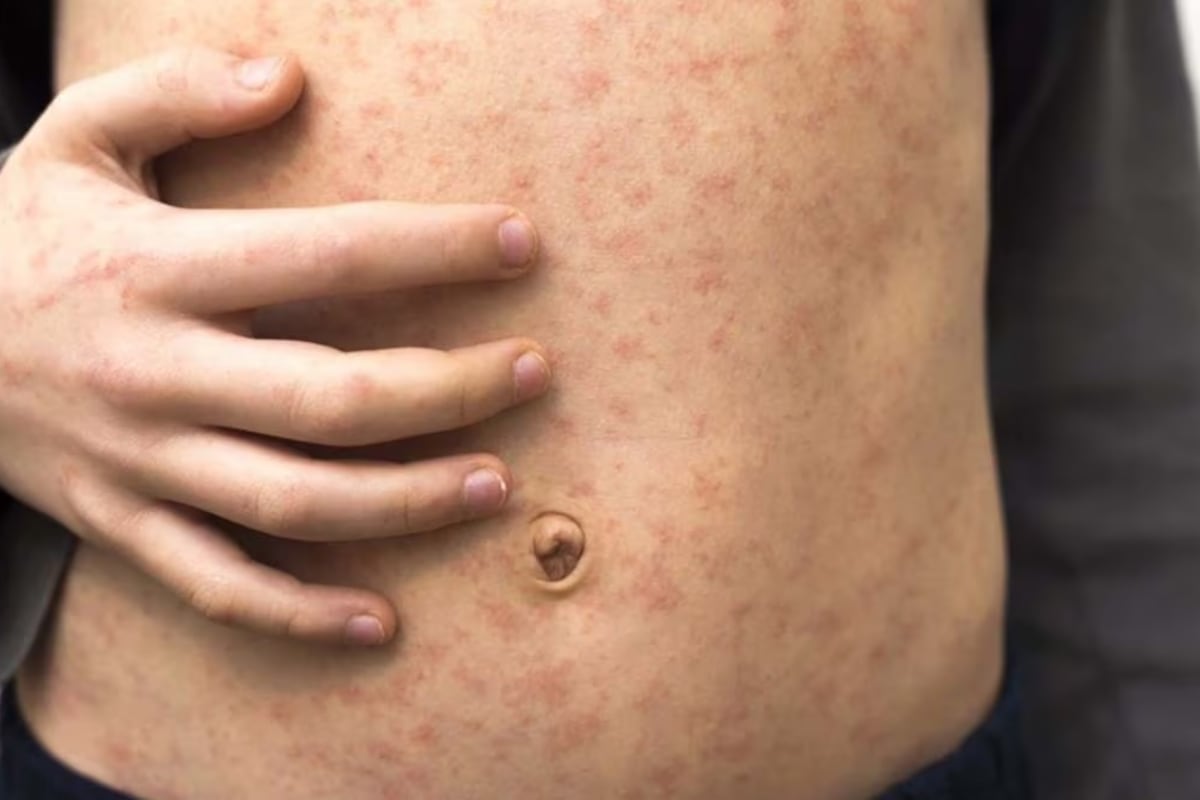
The first symptoms of measles — which include high fever and coughing — appear 7-14 days after catching the virus. A few days after these symptoms, people with the illness often develop small white dots in their mouths and red spots on their face. If Georgia residents notice symptoms for measles, the DPH asks that they call a health care provider before seeking treatment as measles is highly contagious.
Allen Siegler is a reporter covering public health in Atlanta for Healthbeat. Contact Allen at asiegler@healthbeat.org.