Public health, explained: Sign up to receive Healthbeat’s free New York City newsletter here.
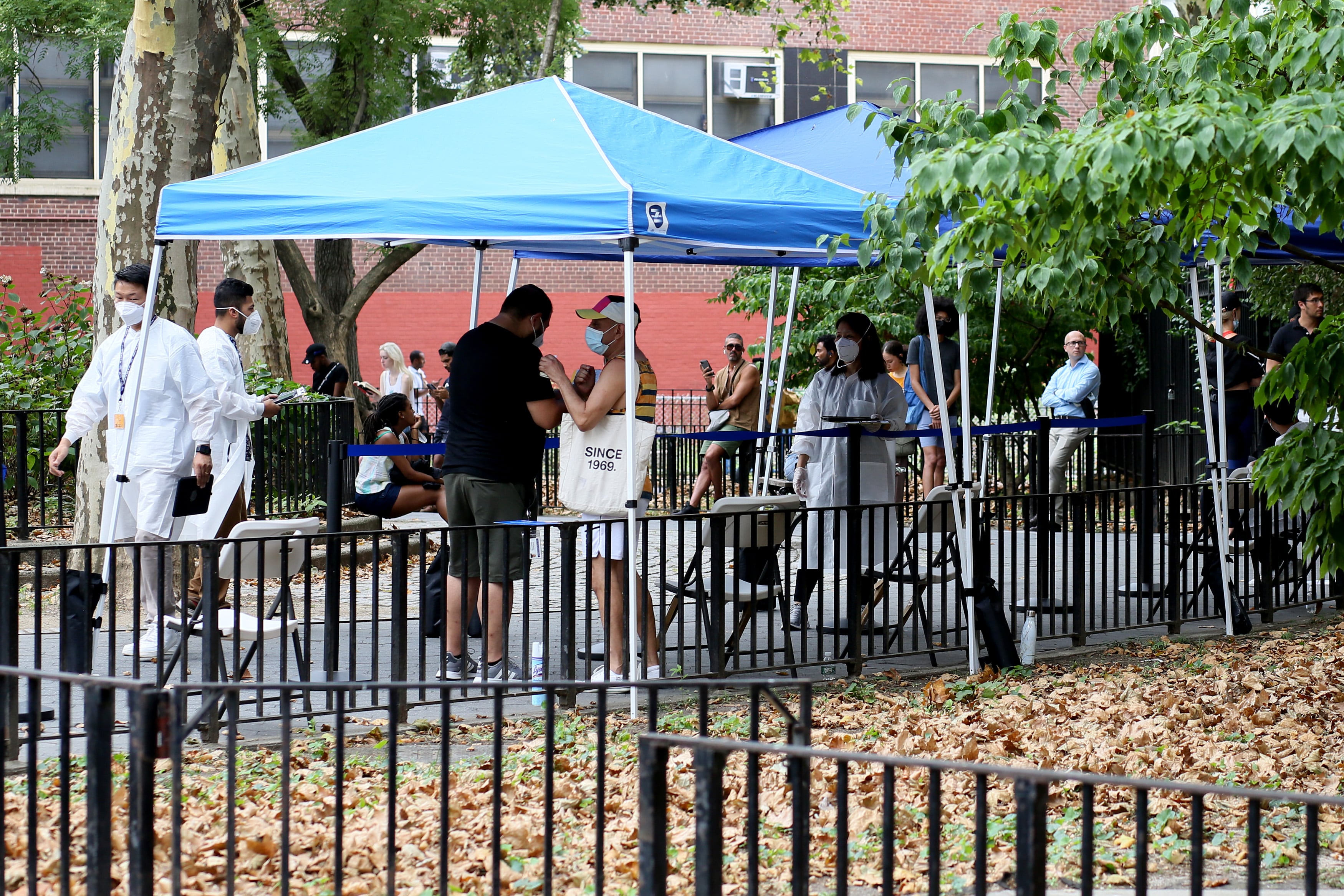
On the heels of the World Health Organization’s declaration of a global emergency for mpox, the New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene on Thursday urged anyone at risk to get vaccinated against the virus.
“We have learned many lessons from the 2022 outbreak, and we are prepared,” Health Commissioner Dr. Ashwin Vasan said in a statement. “While the current risk to New Yorkers and Americans is low, we must not only plan ahead but act now.”
Vasan urged anyone at risk for mpox who has not been vaccinated to do so immediately, noting that two doses are needed for maximum protection. New Yorkers can search for a vaccination appointment on the Health Department’s website.
In 2022, New York City was at the epicenter of the country’s outbreak of mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, which is a close relative of smallpox. The outbreak peaked that summer with nearly 100 cases of the virus each day.
By early 2023, following the vaccination of more than 100,000 New Yorkers — and with the city touting one of the highest vaccination rates in the country among those at risk for the disease — the Health Department declared the outbreak over.
Still, the virus has continued to circulate in small numbers in New York City. Since Jan. 1, 307 people in the city have tested positive for mpox, with 26 cases from July 7 to Aug. 3, according to the Health Department.
Mpox is spread almost exclusively through oral, anal and vaginal sex and other intimate contact, typically through direct contact with the rash or sores of someone who has the virus, according to the Health Department. Other symptoms can include a sore throat, fever and swollen lymph nodes. Symptoms tend to emerge three to 17 days after exposure and last for two to four weeks.
The Health Department recommends vaccination if you have sex with men and identify as male, transgender, nonbinary, genderqueer or gender-nonconforming, or if you consider yourself to be at risk in the future.
Other prevention measures include not having sex or intimate contact if you or your sexual partners have unexplained rashes or sores, reducing your number of sexual partners, and asking partners if they feel sick, the Health Department advises.
Stephen S. Morse, a professor of epidemiology at the Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, said that since mpox generally spreads through direct contact, it is far less transmissible than a virus like Covid-19. Even so, a few travel-related cases can launch a broader outbreak.
“The concern is that it’s still moving,” he said. “It needs to be controlled.”
The mpox virus has two types, Clade 1 and Clade 2. Clade 1 is dominant in current mpox outbreaks in the Democratic Republic of Congo, which have spread to a dozen other African countries. Clade 2 drove the global mpox outbreak in 2022, including New York City’s crisis.
Clade 1 tends to cause a higher number of severe infections and have a higher mortality rate than Clade 2, according to the Department of Health and Human Services. There are currently no known cases of Clade 1 mpox in the United States.
“For New York City, we’ve been there before, and hopefully we can get it right this time,” Morse said.
Eliza Fawcett is a reporter covering public health in New York City for Healthbeat. Contact Eliza at efawcett@healthbeat.org.